Introduction
The manufacturing industry is rapidly going through industrial digital transformation, which will bring significant changes to production systems. In the context of the approaching 2025, the manufacturing industry is experiencing a level of changes that has never been seen before related to the IoT, AI, and Machine Learning. They are redesigning the production processes, making them more effective, and creating new opportunities for development in the manufacturing industry.
The following article focuses on the important factors that may define the digital transformation of the manufacturing industry in 2025. It goes deeper into the nature of this technological change and features some of the most commonly discussed trends such as predictive maintenance, digital twins, and cloud manufacturing solutions. The article also considers the advantages of digitalization, potential ways to address the challenges, and future trends in smart manufacturing. By understanding these trends, manufacturers can position themselves to leverage digital technologies and stay competitive in an expanding connected, and data-driven world.
The Foundations of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
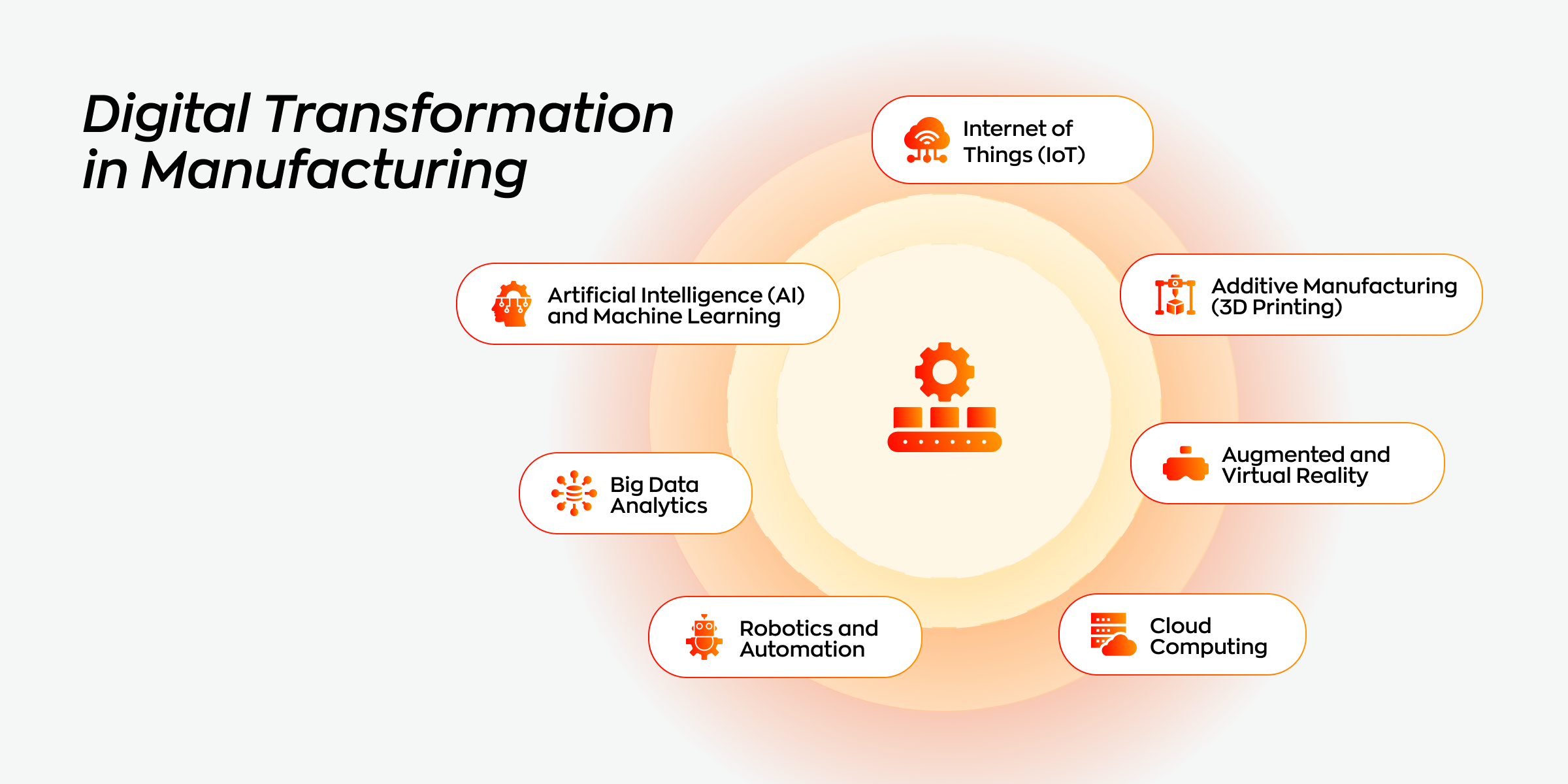
Defining Digital Transformation
Digital transformation (DX) in manufacturing refers to the integration of digital technologies into traditional manufacturing processes to solve challenges, increase efficiency, and create new opportunities. It involves the application of advanced technologies that transform the business model of an organization by redesigning its business activities, products, and services.
Key Technologies Driving Change
Several key technologies are propelling digital transformation in manufacturing:
- Internet of Things (IoT): Integrating IoT devices, such as sensors and connected machinery, enables real-time data collection, predictive maintenance, and optimized production processes.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, automate processes, and drive intelligent decision-making.
- Big Data Analytics: The ability to process and analyze large volumes of data from various sources allows manufacturers to identify trends, improve efficiency, and increase quality control.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud-based solutions, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and manufacturing software, enable remote access, collaboration, and scalable data storage and processing.
- Robotics and Automation: Robotics and automation technologies streamline assembly lines, reduce human error, and increase productivity.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): 3D printing enables the creation of complex and customized products, revolutionizing product design and manufacturing processes.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality: These technologies revolutionize training, maintenance, and design processes by providing immersive and interactive experiences.
Why Digital Transformation is important for manufacturers?
Digital transformation in manufacturing is crucial for organizations to remain competitive in an increasingly digital landscape. According to IDC, global digital transformation (DX) spending is projected to reach nearly $3.9 trillion by 2027, with discrete manufacturing leading all industries in spend. This massive investment underscores the importance of digital transformation in driving efficiency, innovation, and growth within the manufacturing sector.
Digital transformation allows manufacturers to address the key aspects of using digital tools such as IoT, AI, and data analysis in production. The implementation of these technologies can therefore help manufacturers achieve better results in their production processes, quality, and expense levels. For example, IoT sensors offer timely information on the state of a piece of equipment and thus facilitate predictive repair and maintenance. AI and machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify trends and optimize production schedules, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
Furthermore, digital transformation promotes innovation since it provides the manufacturer with the ability to test new ideas for business models and processes. It enables the development of smart factories in which automation and robotics solutions are critical in achieving greater manufacturing flexibility. This shift is equally helpful as it significantly increases the effectiveness of responding to the changing customer needs within the shortest time possible.
In addition to operational benefits, digital transformation also drives significant financial gains. Companies that successfully implement digital strategies often see substantial improvements in revenue and cost savings. According to a McKinsey study, 89% of large companies globally have a digital and AI transformation underway, yet many have only captured a fraction of the potential value. This highlights the critical need for a well-executed digital transformation strategy to fully realize its benefits.
Top Digital Transformation Trends for 2025
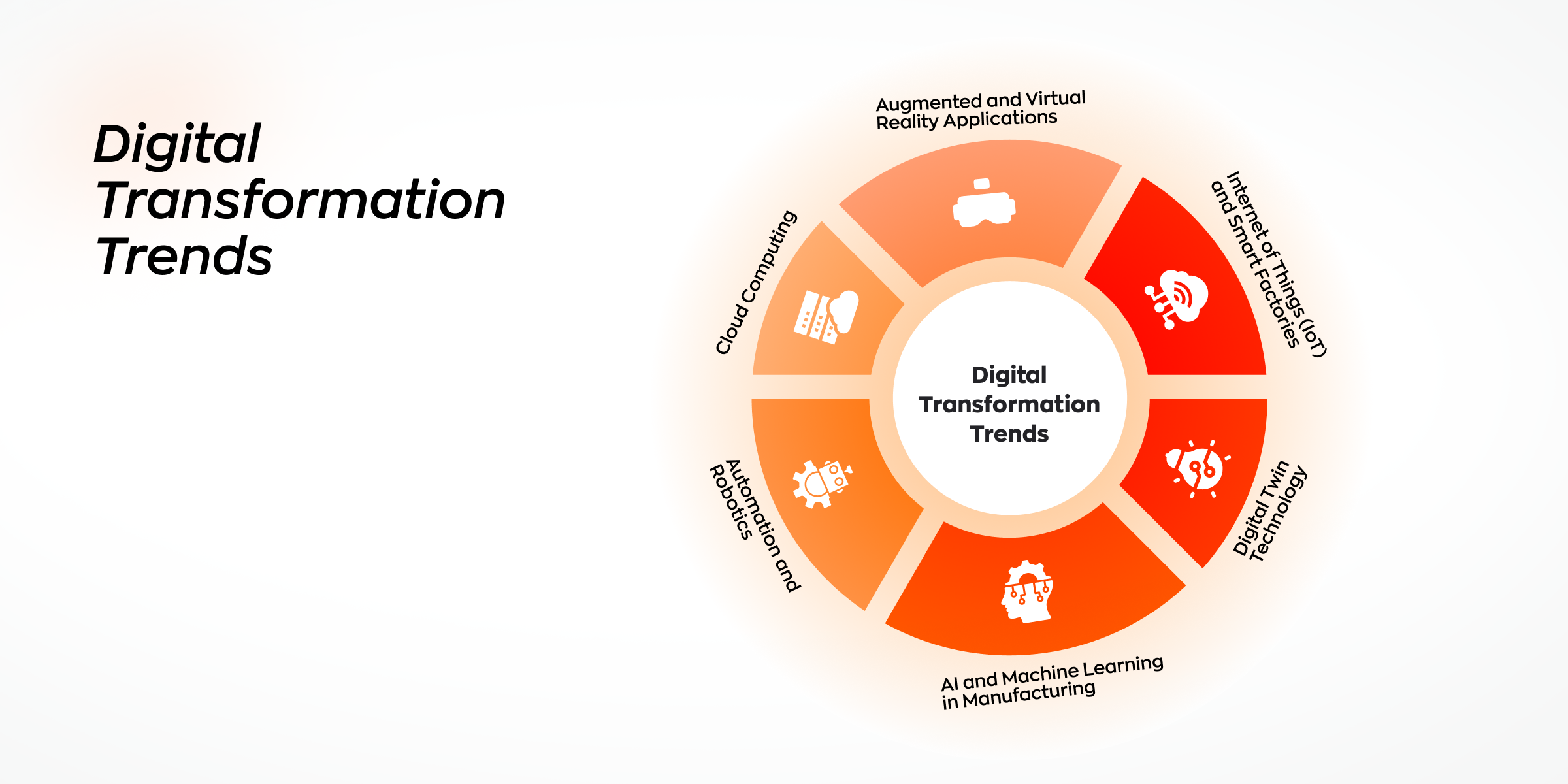
The Internet of Things is the major force behind the shift towards smart factories, whereby machines self-improve and optimize various processes. Sensors and other connected devices like smart machines collect data and provide insights on potential breakdowns and more efficient ways of manufacturing. The IIoT is a proactive system that actively uses the data gathered to enhance operational conditions. Adding artificial intelligence (AI) to IIoT takes the advancements even further, making it possible for machines to offer recommendations concerning process enhancement.
The decreasing cost of IIoT devices facilitates seamless integration for small manufacturers. Cloud technology takes center stage, offering functionalities like remote monitoring and predictive maintenance. Real-time information becomes pivotal for data-driven decisions, with communication protocols like MQTT optimizing industrial setups.
The affordability of 5G technology marks a transformative shift, providing unprecedented speed and minimal latency in cellular technologies. This enables seamless data sharing among IIoT devices, fostering enhanced connectivity. With near-zero latency, 5G revolutionizes remote monitoring, allowing manufacturers to oversee operations remotely and respond swiftly to emerging issues.
AI and Machine Learning in Manufacturing
The impact of AI and machine learning in manufacturing is significant. According to McKinsey, using AI/ML, manufacturers can reduce downtime by up to 50 percent and reduce the costs that come with quality-related issues by up to 20 percent. AI algorithms are more efficient in quality assurance as they involve analyzing large datasets to find out more patterns and inconsistencies. The use of computers and machine learning in vision technology means that only perfect products can be sold in the market since the technology is capable of identifying defects accurately.
By using AI, solutions for the supply chain can be presented with real-time information on demand forecasting, inventory, and logistics. With the help of big data, AI algorithms can work out the problem areas and suggest the best solution on how to minimize costs and manage risks.
Generative AI (GenAI) addresses the shortcoming of dependence on large, labeled datasets for training AI systems. By leveraging GenAI, AI practitioners can create synthetic data to train AI, enabling it to detect defects through visual quality inspection (VQI) systems.
Automation and Robotics
Collaborative robots (cobots) are flexible industrial robots with advanced IT capabilities and integrated safety measures, enabling them to work alongside employees in factories. Cobots can do many tasks, enabling employees to concentrate on creative and more advanced assignments.
However, the current workforce often lacks the necessary skills to deploy and manage these automated systems effectively, resulting in a significant skills gap in the robotics manufacturing industry. To address this issue, several actionable steps can be taken:
- Redesign Education Programs: Integrate advanced robotics and automation technologies into engineering and technical curricula. This should include hands-on modules to provide students with practical experience using the latest equipment and software.
- Industry Collaboration: Establish partnerships between educational institutions and manufacturing companies. These collaborations can facilitate internships, co-op programs, and real-world project work, offering students valuable on-the-job training.
- Professional Development Programs: Provide ongoing training and certification courses for existing professionals. This helps them stay current with emerging technologies and enhances their skill sets to meet industry demands.
- Government and Private Sector Initiatives: Encourage investment in workforce development initiatives. This includes funding for training programs, scholarships for students entering robotics fields, and tax incentives for companies investing in employee education.
By implementing these strategies, the manufacturing industry can develop a skilled workforce capable of driving digital transformation and maintaining a competitive edge in the global market.
Cloud computing is flexible and can be utilized to replace rigid, outdated IT structures of manufacturers with new, cloud-based applications. It reduces machinery servicing time and facilitates easy production expansion by minimizing production time. Cloud-based platforms that integrate machine learning and AI functionalities can process a vast amount of data in real-time to generate real-time predictions for production schedules, product quality, and supply chain logistics.
Cloud-based inventory management systems allow users to monitor stock levels, demand patterns, and supplier performance in real-time, thus preventing overstocking and low stock turnover. Smart sensors installed in the machines collect data on their functioning and transmit it to the cloud where analyzing algorithms look for signs of wear and tear, which helps to reduce the time taken for repairs, the cost of repair, and ultimately increases the lifespan of the machines.
The cloud’s flexible pricing structure means that there is no need to invest large sums of money in hardware, software, and data center upkeep at the beginning of the service. However, under this system, companies are charged for the computing resources that they require, to coordinate with business requirements.
Extended reality (XR) technologies, including augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), are being increasingly adopted in the manufacturing industry. Analysts estimate that utilizing VR/AR technology in the manufacturing sector can provide a $360 billion boost to GDP by 2030, achieved through increased productivity, operational efficiency, and improved production processes.
AR can overlay digital data on top of real-world objects, making it easier for workers to identify defects or deviations from quality standards. AR can be used to train employees on how to perform quality assurance tasks, such as how to properly inspect a product or identify defects. AR can also be used to provide real-time assistance from experienced workers while performing quality assurance tasks, allowing experts to remotely guide workers and ensure that quality standards are met.
VR solutions allow new workers to train in a safe and controlled environment, practicing and learning without the risk of damaging real equipment. VR/AR devices offer features such as eye tracking and hand tracking, which can be used to pinpoint bottlenecks and problems employees face in training.
Digital Twin Technology
Digital twin technology is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape by enabling unprecedented connectivity and data analytics. Digital twins allow for the real-time monitoring and adjustment of production lines, leading to significant reductions in downtime and wastage.
The application of generative AI (GenAI) within digital twins represents a major leap in predictive analytics and simulation. Businesses can now create highly accurate models of their operations, products, assets, or services, enabling them to anticipate outcomes and refine strategies with a much higher degree of precision.
AR and VR technologies are revolutionizing how customers are being engaged since this could not have been imagined some time back. AR/VR serves as a tool through which customer satisfaction is maximized and design and decision-making are made easier when using the 3D content from the digital twin.
Digital twins are at the forefront of promoting sustainability within businesses by accurately modeling energy consumption and the environmental impact of materials and processes, enabling informed decisions that align with sustainability goals.
Benefits of Digital Transformation
Digital manufacturing is revolutionizing the manufacturing sector through the use of digital tools and techniques in the operation of production processes to improve its performance, encourage innovation, and sustain its relevance in the market. The above shift has advantages that are crucial for most manufacturing companies in the contemporary world.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity
The effective implementation of new technologies, including robotic process automation (RPA) and artificial intelligence (AI), contributes to increased performance. These technologies streamline manual work and timely tasks to improve the efficiency of working and provide time for employees to work on complex tasks. For instance, the use of artificial intelligence can be applied to managing production schedules and inventory through resource balancing and efficient time management.
Furthermore, real-time data analysis helps manufacturers to manage production processes in real-time. It makes it possible to correct any mistakes or failures to minimize the production lead time and maximize the efficiency of production. The result is a more agile manufacturing process that can quickly adapt to changing market demands.
- Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
Digital transformation leads to increased operational efficiency by cutting down the costs of using resources and the time spent on a task. One of the key elements of digital transformation is predictive maintenance, which employs data analysis to anticipate failures in machinery. This approach tends to decrease the potential incidences of machines breaking down and reduce the cost of repairs. For example, a company that adopts the use of predictive maintenance may opt to carry out the maintenance at a time when production is not crucial.
In addition, real-time monitoring systems help optimize energy consumption and minimize waste. By analyzing data on energy usage, manufacturers can identify inefficiencies and implement measures to reduce energy costs. This not only lowers operational expenses but also supports environmental sustainability efforts by reducing the carbon footprint of manufacturing operations.
- Improved Quality and Customer Satisfaction
Digital transformation technologies offer manufacturing companies the right tools that they can use to improve the quality of their products and the satisfaction of their clients. Real-time monitoring and control systems enable the detection of defects or process deviations early in the production cycle. This early detection allows for immediate corrective actions, ensuring that only products meeting the highest quality standards are delivered to customers.
Comprehensive product data management systems also play a vital role in maintaining consistency and traceability throughout the production process. Manufacturers should ensure that they have documented every process of production and through such documentation, it becomes easier to notice where there is a glitch in the process of production and correct it without wasting time on guessing.
Moreover, digital transformation initiatives often include customer-focused technologies that enhance the customer experience. For example, manufacturers can use data analytics to gain insights into customer preferences and tailor products to meet specific needs, thereby increasing customer loyalty and satisfaction.
- Enhanced Flexibility and Innovation
Another key benefit that comes with digital transformation is the increase in flexibility within the manufacturing sector. The latest digital technology platforms support the quick change of production lines to allow for the production of new products or models.
Digital transformation also helps create a culture of innovation within manufacturing organizations. By leveraging technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) and big data analytics, manufacturers can explore new business models and revenue streams. For instance, IoT-enabled devices can provide continuous feedback on product performance, offering valuable insights that can drive product improvements and innovation.
- Strategic Alignment and Competitive Advantage
Companies that are following the digital transformation strategies properly can have a competitive advantage as they will be in a better position to respond to changes in the market and customer requirements. For instance, digital tools can help manufacturers in managing the supply chain more efficiently, shortening the lead time and increasing the ability to respond to customer requirements. Digital transformation is deeply connected with other strategic business management concepts like sustainability, market growth, and customer relationship management as it is not only about enhancing operations but also about such key changes.
In addition, embracing digital transformation can help companies improve their brand image and reputation. By showing a commitment to innovation and sustainability, manufacturers can attract environmentally conscious consumers and stand out in a competitive market.
Overcoming Digital Transformation Challenges

- Cost and investment barriers
Manufacturing companies often operate with intricate IT systems comprising diverse hardware, software, and networking components. Managing and integrating these systems to support digital initiatives can be daunting and resource-intensive.
Upgrading from an on-premise solution to a cloud solution has long been an area of concern for decision-makers, primarily because of the perceived risks of hosting company data on cloud servers. However, tier IV data centers offer more security than on-premise servers, meaning data is most secure when hosted on the cloud.
Digital transformation (DX) can be a costly exercise, and it's important not to get wrapped up in a mindset of measuring success with an immediate ROI. The goal is to bring the organization up to speed to stay competitive. A DX strategy for transition should be fully supported and envisioned by key executives and decision-makers in the organization.
- Addressing the Skills Gap
The increased use of digital technologies has created a gap in digital competencies. The demand and supply of skill sets in the workplace have consequently created a digital divide, especially in the manufacturing sector which is experiencing a digital revolution.
Many workers are concerned that digital technologies are taking their jobs and will at some point make them jobless. As a result, there is a notable level of employee resistance or unwillingness to engage with digital devices or software, which only serves to put the workers at a disadvantage. Also, manufacturing organizations are suffering from the digital skills gap, but they can and must do more to address it. Existing employees are valuable members of the organization, and they benefit from company knowledge, relationships, and experience that are worth retaining and developing further.
To thrive in the digital age, organizations need to maintain a solid best-practice foundation and take a continuous improvement approach to transformation. However, before large-scale digital transformation is implemented across the entire organization, it is necessary to assess both digital competencies and overall readiness for change.
To effectively manage the digital skills gap, manufacturers can train a large pool of potential employees. This has the effect of creating the need for organizational members to constantly update their digital skills to keep up with the rapidly evolving technologies, thereby necessary to sustain the competitive advantages that are unique to each organization.
- Managing Data Security and Privacy
The various smart devices and data-driven technologies have made manufacturing companies more sensitive to cyber risks. The implications of cyber threats in relation to production lines, patents, and customers’ information prove the importance of effective cybersecurity measures.
As a result, the risk of cyber-attacks is now one of the most difficult challenges in protecting data security and privacy. Organizations are increasingly being targeted by cybercriminals to steal sensitive data such as financial information, trade secrets, and personal information. A data breach can have devastating consequences, including loss of reputation, financial loss, and legal liability.
Businesses must ensure that personal data is collected, stored, and processed in compliance with various regulations, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and the ePrivacy Directive (Directive 2002/58/EC). These regulations aim to give individuals more control over their data while requiring businesses to be transparent about their data collection and processing practices.
The ePrivacy Directive, which complements the GDPR, specifically regulates the processing of personal data and privacy protection in the electronic communications sector. It requires websites to obtain consent for the use of cookies and similar technologies. The soon-to-be-implemented ePrivacy Regulation is set to replace the Directive and will provide even stricter rules for data processing in electronic communications.
In addition to these EU-wide regulations, each EU member state has its own national data protection laws that may supplement and specify GDPR requirements. Examples include Germany's Bundesdatenschutzgesetz (BDSG) and France's Loi Informatique et Libertés.
Implementing a reliable data governance framework is crucial for achieving data compliance during digital transformation and beyond. This framework should consist of a collection of policies, procedures, and standards for managing and safeguarding data throughout its lifecycle, taking into account the requirements of all applicable regulations.
- Integrating Legacy Systems
Legacy app integration connects existing (and often outdated) software systems with modern solutions or technologies. Such integration reduces manual work, minimizes employee learning curves, enhances data accessibility, and improves decision-making.
The most popular approaches for legacy system integration include Point-to-Point (P2P), Enterprise Service Bus (ESB), Application Programming Interface (API), and Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS).
Legacy system integration can be a solution when the system houses large volumes of critical legacy data, and its migration might cost more than dealing with the drawbacks of old software. At the same time, integration with a newer system would allow unlocking the full value of this data.
Integration is also appropriate in situations where the system offers specific functions that are essential to the company’s operation when considering a merger with another company or when the system works perfectly but requires additional functionalities, a more user-friendly interface or share data for legal reasons. However, the integration of legacy systems can be problematic due to characteristics such as a lack of specialists knowledgeable about the old technology, scant documentation, low quality of data, resistance to change, and security concerns. Legacy apps are vulnerable to cyber threats, so a robust strategy to protect data during and after integration is essential.
The 5 Main Areas of Digital Transformation
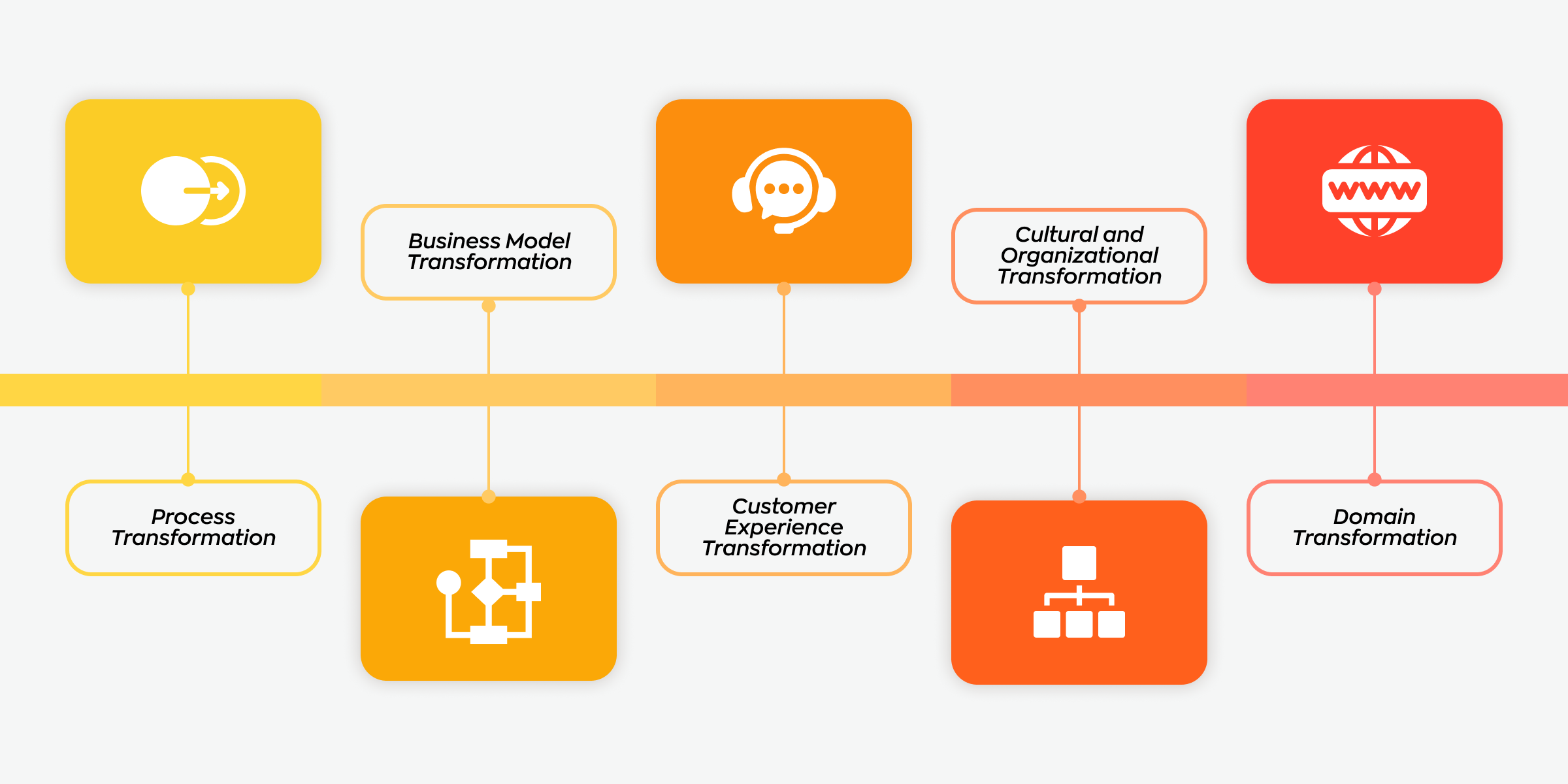
Digital transformation is a comprehensive process that leverages digital technologies to change how businesses operate and deliver value to customers fundamentally. For 2025, manufacturers should focus on five key areas to stay competitive and drive growth.
- Process Transformation. Process transformation involves digitizing and automating existing workflows to make them more efficient and cost-effective. This includes implementing technologies like Robotic Process Automation (RPA), workflow automation, and data analytics to optimize production, supply chain management, and customer service. Steps for Process Transformation:
- Identify Areas for Improvement: Pinpoint business areas that can benefit from digitization, such as production lines or customer service.
- Define Digital Goals: Set specific objectives, like reducing downtime using predictive maintenance with IoT sensors.
- Evaluate Current Processes: Map out existing workflows to identify gaps and waste.
- Select Digital Tools: Choose technologies like RPA and data analytics platforms that align with your business goals.
- Implement Digital Solutions: Integrate new technologies into existing systems.
- Monitor Performance: Use KPIs to track the success of digital initiatives.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and optimize digital solutions to ensure they meet evolving business needs.
- Business Model Transformation. This area leverages digital technologies to create new business models and revenue streams. It involves using digital platforms to connect with customers, developing new digital products and services, and exploring new markets. Examples of Business Model Transformation:
- Digital platforms: Utilizing online platforms to reach customers directly, offering products and services in new ways.
- Modern digital products and services: Developing new offerings tailored to digital-savvy consumers or leveraging digital capabilities, such as subscription services or digital-only products.
- Market expansion: Using digital channels to expand into new markets, either geographically or demographically, to increase reach and relevance.
- Domain Transformation. Domain transformation uses digital technologies to revolutionize entire industries or domains. This includes deploying AI, blockchain, and IoT to create new products, optimize supply chains, and develop new business models. Types of Domain Transformation:
- Industry-Specific: Transform specific sectors.
- Market-Focused: Expand into new markets or serve existing ones more effectively.
- Product/Service: Update the products or services offered.
- Functional: Improve specific business functions like finance or HR.
- Cultural and Organizational Transformation. Creating a culture of digital innovation within the organization is crucial. This involves developing a digital strategy, investing in digital talent, and making an agile organizational structure that can adapt to new technologies and market conditions. Steps for Cultural Transformation:
- Define Scope and Objectives: Identify impacted business areas and desired outcomes.
- Conduct a Gap Analysis: Measure current systems and identify areas for improvement.
- Develop a Roadmap: Outline steps, timelines, and metrics for digital operations.
- Identify Resources: Secure financial, technological, and organizational support.
- Implement the Plan: Execute changes in processes, systems, and infrastructure.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly monitor and refine digital strategies.
- Customer Experience Transformation. Enhancing customer experience through digital means is inevitable for retaining and attracting customers. This involves using data analytics, AI, and personalized marketing to understand customer needs and deliver tailored experiences. Strategies for Customer Experience Transformation:
- Personalization: Use AI to offer personalized recommendations and services.
- Omnichannel Engagement: Ensure a seamless customer experience across all digital and physical touchpoints.
- Feedback Loops: Implement systems to gather and act on customer feedback in real-time.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Analyze and optimize every stage of the customer journey for better satisfaction and loyalty.
By focusing on these five main areas, manufacturers can harness the power of digital technologies to transform their operations, innovate their business models, and improve their customer experiences. The adoption of digital transformation is not just about implementing new technologies; it's about transforming how business is done in the digital age.
Future Trends in Digital Transformation

Evolution of AI and Machine Learning
The innovation of artificial intelligence and machine learning in manufacturing is expected to gain further development. Generative AI (GenAI) models will enable the creation of synthetic data to train AI systems, overcoming the need for large, labeled datasets. This will make it easier to create and use AI tools to check the quality of things, find problems, and plan maintenance.
Moreover, the integration of AI with digital twin technology will unlock new possibilities for predictive analytics and simulation. By creating highly accurate virtual models, businesses can forecast outcomes, optimize processes, and refine strategies with reliability.
The Rise of Smart Factories and Industry 4.0
The concept of smart factories, driven by the Industry 4.0 revolution, will continue to gain momentum. The decreasing cost of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices will lead to seamless integration, even for small manufacturers. Also, cloud technology will play a significant role, enabling remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making.
The adoption of 5G technology will revolutionize industrial connectivity, providing unprecedented speed and minimal latency. This will enable seamless data sharing among IIoT devices, fostering enhanced real-time monitoring and remote operations.
Integration of Advanced Analytics and Big Data
Analytics and big data will become more important over time for manufacturers. Cloud platforms that include machine learning and AI applications will analyze big data in real-time to support predictive analysis for production scheduling, quality assurance, and supply chain management.
Furthermore, the integration of IoT sensors and cloud-based inventory management systems will provide real-time visibility into stock levels, demand forecasts, and supplier performance. This will minimize overstocking, prevent stockouts, and optimize inventory turnover.
Growing Importance of Sustainability and Green Technologies
As environmental concerns continue to rise, the manufacturing industry will prioritize sustainability and green technologies. That’s why digital twin technology will play a crucial role in promoting sustainability by accurately modeling energy consumption and the environmental impact of materials and processes. This will enable informed decisions that align with sustainability goals.
Additionally, the adoption of additive manufacturing (3D printing) will gain traction, reducing material waste and enabling the production of complex, customized products with minimal environmental impact.
Strategies for Successful Digital Transformation
- Assessment and Planning: Evaluating current processes and setting goals
Starting a digital transformation journey requires a comprehensive assessment of current processes, systems, and capabilities. Manufacturers should conduct a thorough analysis to identify areas for improvement and potential opportunities for optimization. This assessment should involve stakeholders from various departments, ensuring a solid understanding of the organization's needs and challenges.
Once the assessment is complete, manufacturers should establish clear goals and objectives for their digital transformation initiatives. These goals should align with the overall business strategy and address specific pain points or desired outcomes, such as increased productivity, reduced costs, improved quality, or enhanced customer experiences.
- Technology Investment: Choosing the right technologies and partners
Selecting the appropriate technologies and solutions is crucial for successful digital transformation. Manufacturers should carefully evaluate different options and consider factors such as scalability, and long-term viability. It is essential to prioritize technologies that align with the organization's specific needs and goals.
Partnering with experienced technology providers and consultants can be beneficial, as they can offer valuable insights, best practices, and expertise in implementing digital solutions. Manufacturers should seek partners with a proven track record in the industry and a deep understanding of the challenges and opportunities unique to their sector.
- Workforce Development: Training and reskilling employees
Digital transformation can only be achieved with the help of a trained and flexible staff. Employers should embrace training and reskilling initiatives so that their employees can acquire the right skills for implementing advanced technologies and strategies. This can include on-the-job training, workshops, online courses, or collaboration with educational institutions.
Effective change management strategies are also critical to ensure a smooth transition and foster a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Engaging employees early in the process, addressing their concerns, and providing ongoing support can help mitigate resistance and promote buy-in for the digital transformation initiatives.
- Data Strategy: Effective data collection, analysis, and cybersecurity measures
Data is at the core of digital transformation, driving insights, decision-making, and process optimization. Manufacturers have to develop a comprehensive data strategy that consists of data collection, storage, analysis, and governance. This strategy should ensure data quality, and accessibility while adhering to relevant regulations and privacy standards.
Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is crucial to protect sensitive data and intellectual property from cyber threats. This includes implementing encryption protocols, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and providing employee training on security best practices.
- Continuous Improvement: Adapting and evolving with technological advancements
Digital transformation is an ongoing process, and manufacturers should embrace a mindset of continuous improvement. As technologies evolve and new advancements emerge, organizations must be prepared to adapt and evolve their strategies and processes accordingly. Establishing a culture of innovation and promoting cross-functional collaboration are essential strategies for creating an environment that nurtures continuous improvement.
Conclusion
As we move towards 2025, the digital transformation in manufacturing is changing the industry landscape, showing significant changes in product design, production, and delivery. The integration of cutting-edge technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing is transforming traditional manufacturing into smart factories. These advancements enable more efficient operations, enhanced customer experiences, and the agility to meet ever-changing market demands.
The shift towards digitalization offers a wide range of benefits, including improved productivity, cost reduction, and the ability to adapt to new challenges and opportunities. However, to fully benefit from these advantages, manufacturers must develop comprehensive strategies that not only focus on technology investment but also emphasize workforce development and robust data management practices. This comprehensive approach ensures that technological advancements are supported by skilled personnel and effective data utilization, leading to sustained improvements.
Embracing a culture of continuous improvement and innovation is crucial for companies aiming to stay competitive in this rapidly evolving landscape. When the management encourages and supports innovative experiments within the company, it will promote the learning and development of new products, services, and business models. This proactive approach not only prepares companies to face emerging challenges but also positions them to capitalize on new market opportunities.
The process of digital transformation is continuous and requires attention to detail and adaptability. Agile manufacturers thrive by embracing change. They upgrade tech, streamline operations, and nurture talent. This forward-thinking approach equips them to navigate today's complex production landscape with confidence.













